Transcendental Meditation Vs Mindfulness Comparison dives into two popular practices that have captured the attention of wellness enthusiasts around the globe. Both offer unique paths to mental clarity and emotional balance, yet they stem from different philosophies and methods. Understanding their roots, techniques, and benefits can help you decide which approach best suits your lifestyle and needs.
In this exploration, we’ll break down the origins and philosophies behind these practices, dissect their techniques, and weigh their health benefits while considering the science backing them. This comparison aims to provide insights that can guide your meditation journey.
Understanding the origins and philosophies of Transcendental Meditation and Mindfulness

Both Transcendental Meditation (TM) and Mindfulness are practices that aim to enhance mental clarity and emotional well-being, yet they stem from vastly different traditions. TM roots itself in the ancient Vedic tradition of India, while Mindfulness finds its origins in Buddhist teachings. Exploring their historical backgrounds and core philosophies reveals the unique pathways they offer towards personal growth and awareness.
Historical Background of Transcendental Meditation
Transcendental Meditation was developed by Maharishi Mahesh Yogi in the mid-20th century, although its roots trace back over 5,000 years to the Vedic texts of ancient India. The Vedic tradition emphasizes knowledge, wisdom, and the pursuit of a deeper understanding of life and consciousness. TM involves the use of a specific mantra, selected for the individual, which is repeated during meditation to facilitate a state of profound rest and relaxation.
This practice is designed to transcend ordinary thinking, allowing individuals to access a deeper level of awareness and inner peace.
Emergence of Mindfulness in Buddhist Practices
Mindfulness, in contrast, has its origins in the teachings of the Buddha, particularly in the concept of ‘sati,’ which refers to awareness and presence in the moment. This practice was systematically developed over centuries, evolving from ancient traditions into contemporary practices. Mindfulness emphasizes observation without judgment, helping individuals cultivate an acute awareness of their thoughts, emotions, and surroundings. Modern adaptations have made Mindfulness accessible, often integrating techniques such as mindful breathing and body scans, which are now utilized in various therapeutic settings.
Core Philosophies Underlying Both Practices
The philosophies behind Transcendental Meditation and Mindfulness, while distinct, share common themes centered on self-awareness and personal growth.
- Transcendental Meditation Philosophy: TM promotes the idea of achieving a unique state of consciousness known as ‘transcendence.’ It emphasizes the importance of quieting the mind to experience inner silence, which can lead to improvements in creativity, stress reduction, and overall mental health.
- Mindfulness Philosophy: The core of Mindfulness lies in being fully present. It encourages individuals to engage with their thoughts and feelings without attachment or aversion, promoting acceptance and compassion towards oneself. This approach can lead to heightened emotional resilience and better coping strategies for stress.
“The goal of Transcendental Meditation is to allow the mind to settle into a state of pure awareness, while Mindfulness encourages living fully in the present moment.”
The distinct origins and philosophies of Transcendental Meditation and Mindfulness provide two powerful avenues for enhancing personal well-being and spiritual growth. By understanding these foundational elements, practitioners can choose the method that resonates more profoundly with their individual journey toward mindfulness and self-exploration.
Exploring the techniques involved in Transcendental Meditation and Mindfulness
Both Transcendental Meditation (TM) and mindfulness are powerful practices that promote mental clarity, emotional well-being, and overall health. However, the way they achieve these benefits differs significantly. In this section, we’ll delve into the specific techniques involved in both TM and mindfulness, highlighting their unique processes and approaches.
Transcendental Meditation Techniques
Transcendental Meditation employs a structured technique primarily centered around the use of a mantra. This is a specific sound or phrase that holds no meaning and is chosen for you by a trained TM teacher. Here’s how the process typically unfolds:
1. Personal Mantra Selection
After a brief introductory session, a TM teacher assigns a unique mantra based on the individual’s age and personal characteristics.
2. Quiet Environment
Practitioners find a comfortable, quiet space where they can sit with their eyes closed, free from distractions.
3. Mantra Repetition
The meditator silently repeats the mantra in their mind, allowing it to guide their consciousness to a deeper state of relaxation and transcendence.
4. Duration
Each session lasts about 20 minutes, typically done twice a day.
5. Effortless Practice
Unlike some meditation styles that require intense concentration, TM encourages a natural, effortless approach, where thoughts can come and go without judgment.
“Transcendental Meditation is not about control; it’s about allowing the mind to settle into a state of restful awareness.”
Mindfulness Practices Overview
Mindfulness encompasses a broader range of techniques that aim to cultivate awareness and presence in the moment. Here’s a closer look at some common mindfulness practices:
Breath Awareness
This practice focuses on observing the natural rhythm of breathing. The goal is to anchor oneself in the present by simply noticing inhalations and exhalations.
Body Scan
In a body scan, practitioners mentally scan their body from head to toe, noticing any sensations, tensions, or areas of comfort. This technique promotes relaxation and awareness of physical sensations.
Mindful Walking
This involves paying attention to the movements of walking, being aware of the sensations in the feet, legs, and the rhythm of the breath as one walks.
Mindful Eating
Practicing mindfulness during meals means focusing entirely on the experience of eating, such as the taste, texture, and aroma of food, without distractions.
“Mindfulness is about being in tune with the present moment, observing without judgment.”
Comparison of Approaches
The key difference between Transcendental Meditation and mindfulness techniques lies in their structure and flexibility. TM follows a precise, structured method that is consistent across practitioners, which can enhance its effectiveness for those who thrive on routine. In contrast, mindfulness offers a more flexible approach, allowing practitioners to choose from a variety of techniques depending on their preferences and circumstances.
This flexibility can make mindfulness more accessible to individuals at different stages of their meditation journey, enabling them to incorporate practices into their daily lives without the need for strict adherence to a specific routine. Ultimately, both practices offer valuable tools for cultivating mental clarity and emotional resilience, and individuals may find that one approach resonates more than the other based on their personal experiences and lifestyle.
Analyzing the mental and physical health benefits associated with each practice
Both Transcendental Meditation (TM) and mindfulness meditation have gained popularity as effective techniques for enhancing mental and physical health. As individuals seek to alleviate stress and improve overall well-being, understanding the specific benefits of these practices can help in making informed choices. Research has shown that both approaches boast a variety of health benefits, albeit with some unique characteristics that set them apart.
Mental Health Benefits of Transcendental Meditation
Transcendental Meditation is primarily recognized for its profound impact on mental health, especially in managing stress and anxiety. Numerous studies highlight its effectiveness in reducing cortisol levels, which is often referred to as the “stress hormone.” For instance, a study published in the journal
Health Psychology* found that participants who practiced TM experienced significant reductions in anxiety compared to those who engaged in control activities.
TM’s structured approach encourages practitioners to focus on a specific mantra, which helps quiet the mind and foster a state of deep relaxation. This technique can lead to long-lasting changes in brain function, promoting improved mood and emotional stability.
“Practicing Transcendental Meditation can lead to a 30% reduction in anxiety levels after just three months.”
Studies also report that TM can enhance resilience against stress, allowing practitioners to cope better with daily challenges. This mental clarity and improved emotional regulation can translate into better decision-making and interpersonal relationships, contributing to overall mental well-being.
Physical Health Advantages Linked to Mindfulness Practice
Mindfulness meditation, while also beneficial for mental health, offers distinct physical health advantages. One of the most notable effects of regular mindfulness practice is improved focus and attention. Research published in
Psychological Science* indicates that mindfulness can enhance cognitive flexibility, which is essential for effective problem-solving and concentration.
Additionally, practicing mindfulness has been linked to improved emotional regulation, helping individuals manage their responses to stressors more effectively. This ability to stay present and aware can lead to lower instances of emotional eating and other unhealthy behaviors.
“Regular mindfulness practice can reduce symptoms of chronic pain and improve overall physical health.”
Moreover, studies demonstrate that mindfulness can lower blood pressure and improve heart health. According to a report from theAmerican Heart Association*, participants who practiced mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques showed significant reductions in hypertension. This suggests that the benefits of mindfulness extend beyond mental clarity and emotional stability, positively impacting physical wellness.
Overall Well-Being Contributions
Both Transcendental Meditation and mindfulness contribute significantly to overall well-being, albeit in unique ways. TM tends to focus more on mental health, providing tools for stress management and emotional stability. In contrast, mindfulness emphasizes present-moment awareness, leading to enhanced focus and physical health benefits. To summarize the distinct contributions of each practice:
- Transcendental Meditation: Reduces anxiety, improves emotional resilience, and fosters mental clarity.
- Mindfulness: Enhances focus, improves emotional regulation, and supports physical health by reducing symptoms of stress-related conditions.
In essence, while both practices are valuable, they cater to different aspects of health and well-being, enabling individuals to choose based on their specific needs and goals.
Investigating the scientific support for Transcendental Meditation versus Mindfulness
When diving into the realm of meditation practices, Transcendental Meditation (TM) and Mindfulness emerge as two prominent approaches, each boasting unique methodologies and benefits. Both have garnered considerable attention in scientific research, highlighting their efficacy in enhancing mental and emotional well-being. Here’s a closer look at the scientific backing behind these techniques, emphasizing their impacts on brain function and cognitive flexibility.
Scientific Studies Supporting Transcendental Meditation
Transcendental Meditation has been the subject of various scientific studies that demonstrate its positive effects on brain function and overall mental health. Research conducted by the American Heart Association indicates that TM can lead to reduced stress and anxiety levels while promoting emotional resilience. One landmark study published in the journalPsychosomatic Medicine* found that participants practicing TM exhibited lower levels of cortisol, a hormone associated with stress.
Furthermore, neuroimaging studies have shown that TM may enhance brain functioning by increasing gray matter volume in areas associated with emotional regulation and cognitive processing, notably the prefrontal cortex. Key findings from recent studies include:
- Increased brain coherence during TM practice, suggesting enhanced communication between different brain regions.
- Improvements in attention and cognitive performance, as evidenced by enhanced scores in standardized cognitive assessments.
- Long-term practitioners of TM report increased levels of creativity and problem-solving abilities, attributed to the practice’s effects on brain function.
“Transcendental Meditation not only reduces stress but also fosters a more resilient brain capable of enhanced cognitive function.”
Research Backing Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness practices, characterized by their emphasis on present-moment awareness, have also seen a robust array of scientific support. Research has consistently shown that engaging in mindfulness can lead to improved cognitive flexibility, which is the brain’s ability to adapt to new situations and think creatively.Studies published in journals such as
- Mindfulness* and
- Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience* reveal that mindfulness meditation correlates with observable changes in brain regions associated with attentional control, emotional regulation, and self-awareness.
Significant findings from the research on mindfulness include:
- Enhanced cognitive flexibility, allowing individuals to shift their thinking and adapt to changing circumstances more easily.
- Increased gray matter density in the hippocampus and areas involved in emotional regulation, leading to better emotional health.
- Improvements in executive functioning, such as decision-making and problem-solving skills, among regular practitioners.
“Mindfulness practices cultivate a flexible mind, empowering individuals to navigate life’s challenges with greater ease and adaptability.”
Comparison of Research Quality and Quantity
When comparing the quantity and quality of research supporting TM and mindfulness, both fields have produced a wealth of studies, but they differ in several respects. TM research, while fewer in number, often features robust methodologies and long-term studies that link TM with significant physiological changes. Conversely, mindfulness research tends to be broader and more diverse, covering a wide range of populations and contexts.
It often employs varied methodologies, including qualitative and mixed-method approaches, which can add depth to understanding its benefits but may also introduce variability in findings.In summary, both Transcendental Meditation and mindfulness are bolstered by scientific evidence, each contributing unique benefits to mental and emotional health. TM emphasizes stress reduction and brain function improvement, while mindfulness enhances cognitive flexibility and emotional resilience.
The ongoing research in both areas continues to illuminate their respective strengths, solidifying their positions in the landscape of mental health practices.
Evaluating the accessibility and training requirements for each practice
Both Transcendental Meditation (TM) and mindfulness offer unique paths to achieving mental clarity and emotional stability, but they come with different accessibility and training requirements. While TM is structured and often requires formal training, mindfulness practices are generally more accessible and can be learned independently. Understanding these aspects can help individuals decide which practice might fit better into their lives.
Transcendental Meditation training requirements
Transcendental Meditation has specific training protocols that set it apart from many other meditation practices. To become a TM practitioner, one must undergo a standardized training process that typically lasts about four days. This includes the following steps:
- Initial Introductory Talk: This is a free session where potential practitioners learn about TM and how it works.
- Personal Instruction: After deciding to learn TM, students attend one-on-one sessions with a certified TM teacher, where they are given a personal mantra.
- Group Sessions: Following personal instruction, students participate in group sessions over the next few days for reinforcement and support.
- Ongoing Support: TM practitioners have access to follow-up sessions and advanced courses, which help deepen their practice.
The structured nature of TM ensures that practitioners receive consistent and thorough guidance, which can enhance the meditation experience. However, this formal training means that TM can be less accessible for those who may not have the time, resources, or desire to commit to a structured program.
Mindfulness accessibility and resources, Transcendental Meditation Vs Mindfulness Comparison
Mindfulness, on the other hand, is remarkably flexible and accessible. It can be practiced almost anywhere and is not confined to a specific setting. There are a plethora of resources available for those interested in learning mindfulness independently, such as:
- Books: Numerous authors, like Jon Kabat-Zinn and Thich Nhat Hanh, have written accessible books on mindfulness.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Headspace offer courses ranging from beginner to advanced levels, often for free or at a low cost.
- Mobile Apps: Mindfulness apps provide guided meditations, reminders, and tracking features to help users stay consistent.
- YouTube Videos: Many mindfulness practitioners share guided meditations and tips through video content, making it easy to start practicing immediately.
The variety of resources allows individuals to tailor their learning experience according to their preferences and schedules, making mindfulness an appealing option for those looking to incorporate meditation into their daily lives.
Ease of adopting each practice for beginners
When it comes to adopting these practices into daily routines, beginners may find mindfulness easier to integrate into their lifestyles. With its emphasis on being present in the moment, mindfulness can be practiced during everyday activities like eating, walking, or even brushing teeth. In contrast, the structured nature of TM may require a more dedicated time slot for practice, as it typically involves a 20-minute session, twice a day, while seated comfortably with eyes closed.
For those just starting out, this commitment might feel daunting.
“Mindfulness can be woven into the fabric of daily life, making it more adaptable for beginners.”
In summary, while Transcendental Meditation offers a structured approach with defined training requirements, mindfulness provides a more accessible, flexible path for those looking to enhance their mental well-being. Each practice has its unique benefits, and understanding the accessibility and training involved can significantly influence the choice of practice for newcomers.
Examining the cultural perceptions and societal impacts of Transcendental Meditation and Mindfulness
Transcendental Meditation (TM) and mindfulness have both carved unique niches in contemporary culture, but their societal perceptions and impacts are quite distinct. TM, with its roots in Eastern spirituality, has often been seen through a Western lens that can sometimes misinterpret its essence. In contrast, mindfulness has woven itself into the fabric of modern wellness movements, finding acceptance in diverse sectors like healthcare and education.
This exploration reveals the cultural implications of these practices and their societal integration.
Cultural Perception of Transcendental Meditation in Western Societies
In Western societies, Transcendental Meditation is often viewed as a blend of mysticism and modern self-help. Initially popularized by figures like the Beatles in the 1960s, TM has encountered a spectrum of reactions ranging from skepticism to enthusiastic embrace. Many appreciate its structured approach, which includes a mantra and a defined practice schedule. However, some critics question its authenticity and commercialization, viewing it as a product of spiritual consumerism.Key perceptions influencing TM’s cultural landscape include:
- Spirituality vs. Commercialization: TM’s commercialization, through courses and merchandise, raises eyebrows about its spiritual integrity.
- Celebrity Endorsements: High-profile endorsements have legitimized TM for some, while others see it as a trend lacking genuine substance.
- Scientific Validation: Research supporting TM’s benefits, such as reduced stress and improved focus, has helped shift perceptions from mystical to practical.
The blend of these factors shapes how TM is integrated into individual wellness journeys and its overall acceptance in various communities.
Societal Acceptance of Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness has gained widespread acceptance across various sectors, particularly healthcare and education. Its non-judgmental, present-moment focus resonates with contemporary issues like stress and anxiety, making it a go-to tool for many. This receptiveness is crucial for fostering environments where mental health is prioritized.Important aspects of mindfulness’s societal integration include:
- Healthcare Integration: Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) programs are now commonplace in hospitals and wellness centers, showing evidence of reducing anxiety and improving patients’ quality of life.
- Education Systems: Schools are increasingly incorporating mindfulness practices into curricula, promoting emotional regulation and focus among students, which is vital in today’s fast-paced learning environment.
- Cultural Adaptation: Mindfulness has adapted to fit Western cultural contexts, often presented as a secular practice, which broadens its accessibility and appeal.
This acceptance of mindfulness in various sectors demonstrates its capacity to evolve and the desire for holistic approaches to well-being.
Influence on Contemporary Wellness Movements
Both Transcendental Meditation and mindfulness have significantly influenced contemporary wellness movements. The rise of holistic health, which considers physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being, aligns closely with the principles of both practices.Key influences include:
- Promotion of Mental Health: Both practices have contributed to a broader societal understanding of mental health, promoting the idea that mental wellness is as crucial as physical health.
- Workplace Wellness Programs: Companies are increasingly adopting mindfulness and TM practices as part of employee wellness initiatives, leading to improved productivity and morale.
- Media and Literature: The surge in books and media focused on mindfulness and TM has popularized these concepts, making them household terms in discussions about wellness.
Their influence is evident in how society approaches health and well-being today, encouraging individuals to seek balance and mindfulness in their everyday lives.
Highlighting personal testimonies and experiences with Transcendental Meditation and Mindfulness
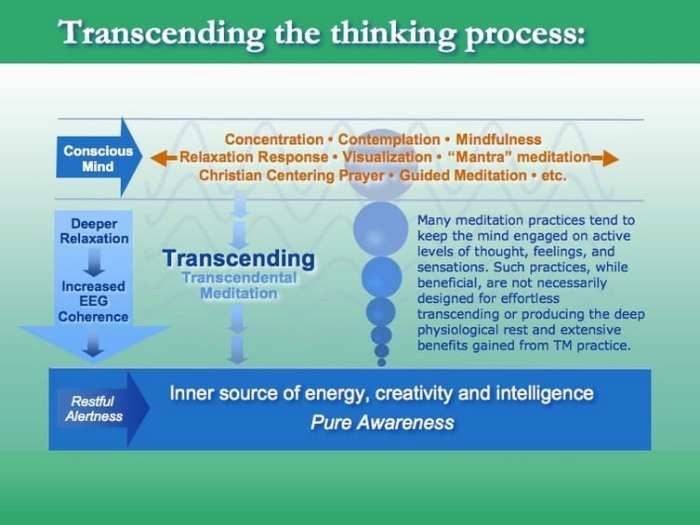
Both Transcendental Meditation (TM) and mindfulness have garnered attention for their unique approaches to mental well-being and personal growth. Practitioners of these techniques often share profound transformations in their lives due to these practices. Exploring personal testimonies not only illustrates the impact of each method but also sheds light on their distinct qualities and benefits.Personal experiences from individuals practicing TM reveal a common thread of deep relaxation and heightened creativity.
TM is often described as a tool that fosters a more profound connection to oneself. For example, a 35-year-old graphic designer shared, “After starting TM, I found that my creativity surged. I could sit down and brainstorm ideas without the usual mental block I experienced before.” This sense of ease and flow was echoed by a retired teacher, who noted, “The stress I carried for years melted away; I now wake up feeling refreshed and ready to embrace the day.”
Experiences with Transcendental Meditation
Transcendental Meditation is known for its simplicity and effectiveness, leading many to report transformative experiences. Here are some notable testimonials from TM practitioners:
- A corporate executive shared, “TM has been a game-changer for my work-life balance. I can approach my job with clarity and focus I never had before.” This reflects how TM can enhance productivity and reduce workplace stress.
- A college student mentioned, “I was overwhelmed with exams and deadlines. My TM practice helped me cultivate a sense of calm that allowed me to study more effectively.” This indicates that TM can significantly benefit academic performance.
- A mother of two expressed, “Finding just 20 minutes for TM each day has transformed my approach to parenting. I feel more patient and present with my kids.” This highlights TM’s role in improving relationships through increased emotional stability.
In contrast, mindfulness practitioners often describe a more conscious awareness of the present moment, which leads to stress reduction and emotional resilience. A yoga instructor stated, “Mindfulness has helped me appreciate the little things. I savor my morning coffee instead of just rushing through it.” This level of awareness allows individuals to connect deeply with their surroundings and experiences.
Experiences with Mindfulness
Mindfulness practice often emphasizes living in the moment and cultivating self-compassion. The following testimonials illustrate the transformative nature of mindfulness:
- A therapist shared, “Incorporating mindfulness into my sessions has not only benefited my clients but has also enriched my personal life. I’ve learned to approach challenges with a calm mindset.” This reflects the reciprocal benefits of mindfulness in both professional and personal contexts.
- A high school teacher reported, “Mindfulness techniques have helped my students manage anxiety, and I’ve seen them flourish as a result.” This underscores the positive impact of mindfulness in educational settings.
- A business owner noted, “Before practicing mindfulness, I was always stressed about my company. Now, I take a moment to breathe and recalibrate, which has improved my decision-making.” This illustrates mindfulness’s potential to enhance leadership and business outcomes.
The transformation narratives from both Transcendental Meditation and mindfulness practitioners reveal their unique aspects. While TM often emphasizes deep relaxation and creativity, mindfulness focuses on present-moment awareness and emotional resilience. These personal experiences contribute to a broader understanding of how each practice can lead to meaningful changes in various aspects of life.
Creating a practical guide for individuals to choose between Transcendental Meditation and Mindfulness
When looking to incorporate meditation into your life, understanding the differences between Transcendental Meditation (TM) and Mindfulness can be a game-changer. Both practices offer unique benefits and can significantly enhance your well-being. However, knowing which one aligns with your personal preferences and lifestyle is crucial to making the most of your meditation journey.To help you navigate this decision, here’s a practical checklist and step-by-step guide to get started.
By assessing your needs and integrating meditation into your daily routine, you can optimize your practice and experience the transformative effects of both techniques.
Checklist for Assessing Meditation Preferences
Before diving into either practice, it can be helpful to evaluate your preferences and lifestyle. Here’s a checklist that can guide your decision:
- Goal Orientation: Identify your primary goals for meditation—stress relief, self-awareness, improved focus, or emotional balance.
- Time Commitment: Consider how much time you can realistically dedicate each day to meditation. TM typically requires 20 minutes twice a day, while Mindfulness can be more flexible.
- Learning Style: Reflect on whether you prefer structured guidance (common in TM) or a more open-ended approach (found in Mindfulness).
- Environment: Think about your preferred meditation environment. TM often benefits from a quiet, distraction-free setting, whereas Mindfulness can be practiced anywhere.
- Personal Beliefs: Evaluate how each practice aligns with your personal beliefs and lifestyle choices.
Step-by-Step Approach for Beginners
Starting meditation can feel daunting, but breaking it down into manageable steps can ease the process. Here’s how beginners can effectively start with either Transcendental Meditation or Mindfulness:
Transcendental Meditation Steps
- Find a Certified Teacher: Look for a certified TM instructor who can provide personal guidance.
- Learn Your Mantra: During your first session, you’ll be given a personal mantra to repeat during meditation.
- Set a Schedule: Aim for 20 minutes of meditation twice a day, ideally in the morning and late afternoon.
- Practice Regularly: Consistency is key; practice daily to reap the benefits.
- Reflect on Your Experience: After each session, take a moment to notice any changes in your thoughts or feelings.
Mindfulness Steps
- Begin with Breathing: Start by focusing on your breath for a few minutes to anchor yourself.
- Practice Body Scanning: Gently shift your focus through your body, noticing sensations without judgment.
- Engage in Mindful Activities: Incorporate mindfulness into everyday tasks, such as eating, walking, or even washing dishes.
- Build Duration Gradually: Start with short sessions of 5-10 minutes and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable.
- Join a Group or Class: Consider participating in local or online mindfulness groups for support and guidance.
Integrating Meditation into Daily Routine
To ensure you get the most out of your chosen meditation practice, it’s essential to integrate it into your daily life. Here are some practical tips for making meditation a regular part of your routine:
- Set a Specific Time: Designate a specific time each day for your practice, making it a non-negotiable part of your schedule.
- Create a Dedicated Space: Establish a comfortable and inviting spot in your home that’s solely for meditation.
- Use Reminders: Set reminders on your phone or leave notes in visible spots to encourage consistency.
- Pair with Existing Habits: Link your meditation time with daily activities, such as brushing your teeth or having your morning coffee.
- Be Flexible: Life gets busy; if you miss a session, don’t stress. Just get back on track when you can.
“The best time to meditate is when you don’t feel like it.”
End of Discussion
In summary, both Transcendental Meditation and mindfulness present valuable tools for enhancing well-being. Whether you lean towards the structured mantra-based approach of Transcendental Meditation or the flexible, everyday applications of mindfulness, incorporating either into your routine can lead to profound personal transformations. The choice ultimately depends on your preferences, lifestyle, and what resonates most with you.
Answers to Common Questions: Transcendental Meditation Vs Mindfulness Comparison
What is Transcendental Meditation?
Transcendental Meditation is a specific form of silent mantra meditation that involves the repetition of a particular sound or phrase to achieve a state of deep relaxation and mental clarity.
How does mindfulness differ from Transcendental Meditation?
Mindfulness focuses on being present and aware of thoughts and sensations as they occur, while Transcendental Meditation emphasizes the use of a mantra to transcend ordinary thinking.
Can I practice both Transcendental Meditation and mindfulness?
Yes, many people incorporate both practices into their routines to benefit from the unique advantages each offers.
Do I need a teacher to learn Transcendental Meditation?
Yes, Transcendental Meditation typically requires learning from a certified teacher to ensure proper technique and understanding.
Is mindfulness accessible for beginners?
Absolutely! Mindfulness practices can be easily learned through resources like apps, books, and online courses, making them highly accessible to beginners.