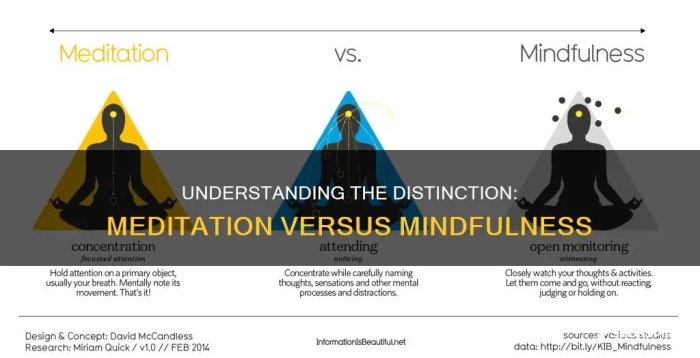
Difference Between Mindfulness And Meditation Explained, let’s dive deep into these two practices that are often thrown around interchangeably but hold distinct meanings and benefits. Both mindfulness and meditation have roots in ancient traditions, yet they cater to different needs and approaches. Understanding their unique principles can empower you to incorporate them into your daily life effectively.
Mindfulness is all about being present and fully engaging with the moment, while meditation involves focused practices designed to develop concentration, clarity, and emotional positivity. This overview will help you grasp how these practices differ, what they share, and how they can each enhance your mental well-being.
Understanding Mindfulness and Its Core Principles
Mindfulness is more than just a buzzword; it’s a practice that encourages us to be fully present in the moment. Rooted in ancient Eastern traditions, particularly Buddhism, mindfulness has gained traction in the West as a powerful tool for enhancing mental well-being and reducing stress.At its core, mindfulness involves maintaining a moment-to-moment awareness of our thoughts, feelings, bodily sensations, and surrounding environment.
It encourages an attitude of openness and non-judgment towards whatever arises. This practice can help cultivate a more profound sense of calm and clarity, allowing individuals to respond to life’s challenges with greater ease.
Key Principles of Mindfulness Practice
Mindfulness is built upon several fundamental principles that guide practitioners in their journey toward greater awareness. Understanding these principles is essential for anyone looking to incorporate mindfulness into their life.
- Awareness: The foundation of mindfulness practice involves being aware of what is happening in the present moment. This includes tuning into physical sensations, thoughts, and emotions without distraction.
- Non-judgment: Mindfulness encourages observing experiences without labeling them as good or bad. This non-judgmental approach fosters acceptance and can lead to a more positive mental state.
- Acceptance: Instead of resisting discomfort or unpleasant feelings, mindfulness teaches individuals to accept their experiences. This acceptance can reduce the stress associated with trying to avoid difficult emotions.
- Focus on Breath: Breathing serves as an anchor in mindfulness practice, helping to bring attention back to the present moment whenever distractions arise.
Examples of Mindfulness Techniques
Integrating mindfulness into daily life doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are a few straightforward techniques that anyone can adopt to enhance their mindfulness practice.
- Mindful Breathing: Take a few minutes each day to focus on your breath. Notice the sensation of air entering and leaving your nostrils, and if your mind wanders, gently bring it back to your breath.
- Body Scan: Lie down comfortably and mentally scan your body from head to toe, noticing any areas of tension or discomfort. This practice can help build awareness of physical sensations.
- Mindful Eating: During meals, pay close attention to the flavors, textures, and aromas of your food. Chew slowly and appreciate each bite instead of rushing through your meal.
- Walking Meditation: Take a leisurely walk, focusing on the sensation of your feet touching the ground and the rhythm of your movement. Let go of distractions and immerse yourself in the experience of walking.
“Mindfulness is a way of befriending ourselves and our experience.”
Jon Kabat-Zinn
Through these simple yet effective techniques, individuals can cultivate a greater sense of presence and improve their overall mental health. Mindfulness invites us to slow down, observe, and appreciate the richness of our lives, one moment at a time.
Defining Meditation and Its Historical Context
Meditation is a practice that has deep roots in various cultures and traditions, often seen as a pathway to self-discovery and inner peace. Its significance transcends mere relaxation; it serves as an instrument for spiritual growth, mental clarity, and enhanced emotional well-being. Across different epochs and communities, meditation has been utilized not just for personal development, but also as a tool for social cohesion and cultural identity.Historically, meditation dates back thousands of years, with its origins rooted in ancient Eastern philosophies.
It is prominently featured in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Taoism, where it has been intertwined with religious practices and rituals. The core essence of meditation involves focusing the mind to achieve a state of mental clarity and emotional stability. While the techniques may differ, the fundamental goal remains the same: to cultivate awareness and presence in the moment.
Different Forms of Meditation and Their Unique Characteristics, Difference Between Mindfulness And Meditation Explained
There are numerous styles of meditation, each with its own techniques and goals. Understanding these forms can help individuals find the style that resonates best with them. Below is a breakdown of some popular meditation types, along with their distinct features:
| Meditation Style | Purpose | Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Mindfulness Meditation | Increase awareness of the present moment | Observing thoughts and sensations without judgment |
| Transcendental Meditation | Achieve deep relaxation and transcend ordinary thought | Repeating a specific mantra |
| Zen Meditation (Zazen) | Develop insight through seated meditation | Focusing on breath and posture, often in silence |
| Loving-Kindness Meditation (Metta) | Foster compassion and kindness towards oneself and others | Reciting phrases of goodwill towards oneself and others |
| Vipassana Meditation | Gain insight into the nature of reality | Awareness of bodily sensations and examining thoughts |
Each of these meditation styles offers unique benefits, allowing practitioners to explore different aspects of their consciousness and emotional landscape. By engaging with these practices, individuals can cultivate a lasting sense of peace and resilience, regardless of their background or beliefs.
“Meditation is the discovery that the point of life is always arrived at in the immediate moment.” – Alan Watts
Comparing the Objectives of Mindfulness and Meditation

Mindfulness and meditation, though often used interchangeably, serve distinct purposes and objectives in the realm of mental health and personal development. Understanding these differences can enhance the effectiveness of your practice and cater to specific needs. Mindfulness is primarily about being present in the moment and developing an awareness of one’s thoughts, feelings, and surroundings. It focuses on cultivating a non-judgmental space where individuals can observe their experiences as they arise.
On the other hand, meditation is typically more structured and often involves specific techniques aimed at achieving a state of deep relaxation or heightened awareness. The objectives here can vary widely, including reducing stress, enhancing focus, or achieving spiritual growth.
Primary Objectives of Mindfulness Practices
The primary objectives of mindfulness practices are centered around awareness and acceptance. By incorporating mindfulness into daily routines, practitioners aim to achieve the following:
- Enhanced Awareness: Mindfulness encourages individuals to engage fully with their present experiences, fostering a deeper understanding of their internal and external environments.
- Emotional Regulation: Practicing mindfulness helps in recognizing and responding to emotions in a constructive way, reducing impulsivity and reactivity.
- Stress Reduction: By focusing on the present, mindfulness can significantly reduce anxiety and stress levels, helping individuals to cope better with daily challenges.
- Improved Relationships: Mindfulness promotes empathy and compassion, often leading to healthier interactions with others and improved communication skills.
Primary Objectives of Meditation Practices
Meditation practices, while also fostering awareness, often have more specific and varied goals. The key objectives include:
- Deep Relaxation: Many meditation techniques are designed to induce a state of relaxation that calms the mind and body, which can aid in sleep and stress relief.
- Focus and Concentration: Certain forms of meditation, like concentration meditation, aim to improve attention span and mental clarity, which can enhance productivity.
- Spiritual Growth: For some, meditation serves as a pathway to deeper spiritual understanding and connection, often involving reflection and insight.
- Mind-Body Connection: Meditation fosters a stronger connection between the mind and body, which can be beneficial in practices such as yoga and tai chi.
Case Studies and Testimonials
Real-life examples illustrate the practical benefits of mindfulness and meditation, showcasing how each approach can cater to different needs. One notable case is a study involving corporate employees who adopted mindfulness training. The results showed a significant decrease in stress levels, increased job satisfaction, and improved productivity. Participants reported feeling more present and engaged in their work, highlighting mindfulness’s role in enhancing workplace dynamics.Conversely, a testimonial from a long-term meditator reveals the profound impact of meditation on personal well-being.
This individual shared that daily meditation practice not only alleviated symptoms of anxiety but also provided a sense of inner peace and clarity, enabling them to navigate life’s challenges with greater ease.These examples underline that while mindfulness and meditation share common ground, the distinct objectives they serve can profoundly affect practitioners’ experiences and outcomes. By aligning practices with personal goals, individuals can harness the full potential of both mindfulness and meditation to enhance their quality of life.
The Role of Awareness in Mindfulness vs. Meditation
Awareness plays a crucial role in both mindfulness and meditation, yet the way it is cultivated and utilized differs significantly between the two practices. Understanding these differences can help individuals better integrate both techniques into their lives, enhancing overall well-being and mental clarity.In mindfulness, awareness is about being fully present in the moment and acknowledging one’s thoughts and feelings without judgment.
This heightened state of awareness allows individuals to engage more deeply with their daily experiences. For instance, when practicing mindfulness while eating, one pays close attention to the taste, texture, and aroma of the food, which can lead to a more satisfying and enjoyable experience. This practice fosters a greater appreciation for the present, reducing stress and improving emotional regulation.
Awareness Process in Meditation Techniques
The awareness process in meditation varies widely depending on the technique used. While some methods emphasize focusing on breath or a specific object, others encourage the observation of thoughts as they arise. The common thread, however, is the cultivation of a focused, calm awareness that allows for greater insight into one’s mental processes. Different meditation techniques foster awareness in unique ways.
For example, in mindfulness meditation, practitioners may focus on their breath and return to it whenever distractions arise, thereby enhancing concentration and awareness of their thoughts. On the other hand, loving-kindness meditation invites practitioners to cultivate feelings of compassion and love, which promotes a different type of awareness concerning one’s emotions and their impact on others.To enhance awareness in both mindfulness and meditation practices, here’s a list of effective exercises that encourage greater mental presence and clarity:
Mindful Breathing
Sit comfortably in a quiet space.
Close your eyes and take a deep breath in through your nose.
Focus your attention on the sensation of the breath entering and leaving your body.
- Return your focus to your breath whenever distractions arise.
- Body Scan
Lie down comfortably and close your eyes.
Start from your toes and slowly move your attention up to your head.
Notice any sensations, tensions, or areas of relaxation in each part of your body.
- Acknowledge these feelings without judgment.
- Mindful Walking
Find a quiet space where you can walk slowly.
Focus on the sensation of your feet touching the ground and the movement of your legs.
- Pay attention to your surroundings—the sounds, smells, and sights around you.
- Gratitude Journaling
Each day, write down three things you are grateful for.
Reflect on why you appreciate these things and how they impact your life.
- This practice helps cultivate awareness of positive aspects in daily experiences.
- Meditative Visualization
Sit or lie down in a comfortable position.
Close your eyes and visualize a peaceful scene (like a beach or forest).
Engage all your senses—what do you see, hear, feel, and smell?
Allow this scene to bring you a sense of calm and presence.
Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can significantly enhance your awareness, contributing to a more mindful life and a deeper meditation practice. By understanding the nuances of awareness in both mindfulness and meditation, you can tailor your approach to fit your personal needs and preferences.
The Emotional and Psychological Benefits of Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation are more than just buzzwords; they offer profound benefits for emotional and psychological health. By integrating these practices into daily life, individuals can experience a significant reduction in stress and anxiety, leading to a more balanced and fulfilling life. Let’s dive into how mindfulness enhances emotional well-being and explore the psychological advantages offered by meditation.
Emotional Health Benefits of Mindfulness
Mindfulness encourages individuals to stay present in the moment, which can lead to greater emotional regulation and resilience. Practicing mindfulness allows people to observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment, which can diminish the intensity of negative emotions. This awareness helps in recognizing emotional triggers and reduces impulsive reactions. For instance, someone who is mindful may find themselves less reactive to stressful situations at work, allowing them to respond with calm rather than frustration.
They might approach conflicts with a clearer mindset, focusing on solutions instead of getting caught up in emotional turmoil.
Psychological Advantages of Practicing Meditation
Meditation has been extensively researched, with numerous studies demonstrating its positive impact on mental health. Neuroimaging studies show that regular meditation can alter brain structure, increasing gray matter density in areas related to emotional regulation and stress response. Scientific findings suggest that meditation can lead to reductions in anxiety, depression, and even chronic pain.
- A study published in JAMA Internal Medicine found that mindfulness meditation programs can significantly improve anxiety, depression, and pain.
- Research from Harvard University indicates that mindfulness meditation can actually change the brain’s gray matter, promoting a healthier emotional state.
Scenarios for Relief Through Mindfulness and Meditation
Both mindfulness and meditation can provide relief in various mental health scenarios. Here’s a look at some situations where these practices can be particularly beneficial:Understanding these scenarios can help individuals recognize when to embrace mindfulness or meditation as tools for managing their mental health.
- Stressful work environments where deadlines create anxiety.
- Moments of anger or frustration during conflicts with friends or family.
- Pre-exam jitters or performance anxiety before public speaking.
- Feelings of sadness or depressive thoughts during low periods.
- Overwhelm caused by balancing multiple responsibilities in daily life.
Practical Tips for Starting a Mindfulness Practice
Mindfulness can seem overwhelming at first, but starting a practice doesn’t have to be complicated. It’s about being present and aware of your thoughts and feelings without judgment. This section will guide you through practical steps to integrate mindfulness into your daily routine, address common challenges you might face, and provide resources to help you along the way.
Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Beginning a mindfulness practice involves simple steps that can easily fit into your daily life. Here’s a straightforward guide to get you started:
- Find a Quiet Space: Select a place where you feel comfortable and won’t be disturbed. This can be anywhere from a cozy corner in your home to a serene spot in a park.
- Set Aside Time: Dedicate a specific time each day. Even five minutes is enough to start. Consistency is key, so try to practice at the same time each day.
- Start with Breathing: Focus on your breath. Inhale deeply through your nose, hold for a moment, and exhale slowly through your mouth. Notice how your body feels with each breath.
- Notice Your Thoughts: As you breathe, thoughts will come and go. Acknowledge them without judgment and gently bring your focus back to your breath.
- Gradually Increase Duration: Once you’re comfortable, gradually increase the time spent in mindfulness practice. Aim for 10-15 minutes as you grow more accustomed.
- Incorporate Mindfulness into Daily Activities: Bring mindfulness into your day-to-day by focusing fully on tasks such as eating, walking, or even showering. Pay attention to the sensations and experiences.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Starting a mindfulness practice can come with its own set of hurdles. Recognizing these challenges and knowing how to address them can make all the difference in sustaining your practice.
“It’s normal to feel restless or distracted at first.”
Many beginners find it difficult to quiet their minds. When distractions arise, gently return your focus to your breath without frustration. This is part of the practice.
“Establishing a routine can be tough.”
Life can get busy, and setting aside time for mindfulness can slip through the cracks. To combat this, schedule your mindfulness time in your calendar, just like any other important appointment.
“Impatience can lead to discouragement.”
Mindfulness is a skill that takes time to develop. If you find yourself feeling impatient, remember that progress doesn’t always look the same for everyone. Celebrate small victories along the way.
Resources for Developing a Mindfulness Routine
To enhance your mindfulness practice, consider utilizing books, apps, and websites designed specifically for beginners. Here’s a summary table of some valuable resources:
| Resource Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Book | The Miracle of Mindfulness | By Thich Nhat Hanh, this book offers practical exercises and insights into living mindfully. |
| App | Headspace | A user-friendly app that provides guided meditations and mindfulness practices, tailored to various needs. |
| Website | Mindful.org | A comprehensive resource filled with articles, tips, and guided practices for cultivating mindfulness in everyday life. |
Techniques for Incorporating Meditation into Daily Life
Integrating meditation into your daily routine can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be a chore. With the right techniques, you can blend meditation seamlessly into your lifestyle, making it a natural part of your day rather than a task on your to-do list.Designing a personalized meditation routine means considering your individual lifestyle, preferences, and schedule. Here are some key methods to help you create a routine that works for you and tackle any obstacles that might pop up along the way.
Creating a Personalized Meditation Routine
To start crafting your unique meditation practice, reflect on when and where you feel most comfortable meditating. Establishing a consistent schedule can significantly enhance your experience. Consider these points when building your routine:
- Identify Optimal Times: Look for natural pauses in your day, such as early mornings, lunch breaks, or evenings, to dedicate to meditation.
- Choose a Comfortable Space: Find a quiet spot in your home or outdoors that you associate with calmness, free from distractions.
- Set Realistic Durations: Start with short sessions (5-10 minutes) and gradually increase as you become more comfortable. This way, you won’t feel pressured to commit to long sessions right away.
- Incorporate Different Techniques: Try various types of meditation, including mindfulness, loving-kindness, or guided meditations, to find what resonates with you.
Overcoming Obstacles to Regular Practice
It’s common to face obstacles that disrupt your meditation practice. Recognizing these hurdles is the first step in overcoming them. Here are some strategies to help you stay committed:
- Set Clear Intentions: Remind yourself of the benefits of meditation; this can motivate you to keep going even when life gets busy.
- Use Reminders: Setting alarms or notifications on your phone can prompt you to meditate, making it easier to stick to your schedule.
- Buddy System: Find a meditation partner to share your experiences and hold each other accountable, boosting motivation.
- Be Flexible: Life can be unpredictable; if you miss a session, don’t beat yourself up. Just adjust and keep moving forward.
Structured Daily Meditation Schedule
Developing a structured daily meditation schedule can help you establish a consistent practice. Here’s a sample plan to get you started:
| Time | Duration | Type of Meditation |
|---|---|---|
| Morning (7:00 AM) | 10 minutes | Mindfulness Meditation |
| Midday (12:30 PM) | 5 minutes | Breath Awareness |
| Evening (8:00 PM) | 15 minutes | Guided Relaxation |
Creating a structured schedule allows you to experience the benefits of meditation while also fitting it into your day-to-day life. With a bit of planning and commitment, meditation can become a rewarding and enriching part of your daily routine.
The Science Behind Mindfulness and Meditation
Research into mindfulness and meditation reveals fascinating insights about their impact on the brain and emotional well-being. Numerous studies have shown that these practices not only help reduce stress but also enhance cognitive functions and emotional regulation. Let’s dive into some of the science that supports these benefits.
Research Studies on Brain Impact
Several groundbreaking studies have explored how mindfulness and meditation shape our brains. For instance, research conducted at Harvard University found that individuals who practiced mindfulness meditation showed an increase in gray matter density in brain regions associated with memory, sense of self, empathy, and stress regulation. This suggests that regular practice can lead to structural changes in the brain that may enhance emotional well-being and cognitive abilities.Moreover, a study published in the journal “Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging” indicated that participants who engaged in an 8-week mindfulness-based stress reduction program exhibited significant decreases in the amygdala’s size, which is the brain’s emotional center.
This reduction correlates with improved stress response and emotional regulation, underscoring how meditation practices can alter brain structure and function over time.
Neuroscience Supporting Cognitive Function and Emotional Regulation
Neuroscience has provided compelling evidence of the benefits of mindfulness and meditation for cognitive functions and emotional regulation. Key findings include:
- Improved Attention Span: Research shows that mindfulness practitioners have enhanced focus and attention. They are better at maintaining attention on tasks without succumbing to distractions.
- Emotional Resilience: Studies indicate that individuals who meditate regularly can handle emotional challenges more effectively, leading to reduced anxiety and depression.
- Enhanced Memory and Learning: Meditation has been found to support working memory and cognitive flexibility, allowing for better problem-solving skills and creativity.
- Reduced Stress Levels: Mindfulness practices activate the relaxation response, which lowers cortisol levels and helps mitigate the effects of stress on the brain.
These findings highlight how neuroscience not only backs but also elucidates the significant advantages of incorporating mindfulness and meditation into daily routines.
Infographic Concept: Key Statistics and Findings
An infographic that visually represents the key statistics and findings related to mindfulness and meditation might include the following elements:
Title
The Transformative Power of Mindfulness and Meditation
Key Statistics
“Increase in Gray Matter”
A visual representation showing the upsurge in gray matter density in key areas of the brain (like the prefrontal cortex), with percentages illustrating the change before and after an 8-week program.
“Stress Reduction”
A bar graph showcasing cortisol level changes in meditation practitioners versus non-practitioners during stressful tasks.
“Emotional Health Benefits”
Pie charts breaking down the percentage of individuals reporting lower anxiety and depression symptoms after consistent practice.
“Attention Improvement”
A comparison of attention span statistics between individuals who meditate and those who do not, depicted in a clear, engaging format.This infographic would not only serve as an eye-catching summary of the research but also provide easily digestible data that emphasizes the importance of mindfulness and meditation in modern life.
Conclusion
In summary, while both mindfulness and meditation promote mental wellness, they do so through different pathways. Mindfulness encourages us to live in the now, while meditation invites us to explore our inner landscapes. Understanding these differences can lead to a more tailored approach in utilizing each practice to foster emotional and psychological health, ultimately enriching our daily lives.
FAQ Guide: Difference Between Mindfulness And Meditation Explained
What is the main difference between mindfulness and meditation?
Mindfulness focuses on being present in the moment, while meditation is usually a structured practice aimed at achieving a specific mental state.
Can you practice mindfulness without meditating?
Absolutely! Mindfulness can be practiced in everyday activities like eating or walking, without a formal meditation session.
How long should I meditate for beginners?
Beginners can start with as little as 5-10 minutes a day and gradually increase the duration as they get more comfortable.
Is mindfulness beneficial for stress relief?
Yes, mindfulness is proven to reduce stress by helping individuals focus on the present rather than worrying about the past or future.
Can mindfulness and meditation be practiced together?
Definitely! Many people find that practicing mindfulness during meditation enhances their experience and effectiveness.